COMMON HAIR PROBLEMS
Common problems affecting the hair and scalp include hair loss, infections, and disorders causing itching and scaling.
Hair loss (alopecia) is a frequent concern for both men and women, although it is normal to shed some hair each day. People who experience more than normal hair loss may have the inherited tendency to "common baldness." Male pattern baldness is the most common cause of hair loss in men, with a receding hair line and baldness on the top of the head. Women may develop female pattern baldness in which the hair becomes thin over the entire scalp. Alopecia areata causes hair loss in small, round patches while tight elastics or braids may cause hair loss at the hairline (traction alopecia). Certain diseases (eg, thyroid problems, diabetes, and lupus), medicines, or poor nutrition may also cause hair loss.
Infections of the scalp include bacterial infection of hair follicles (folliculitis), infestation of head lice (pediculosis capitis), and fungal infection of scalp ringworm (tinea capitis). Itching and excessive flaking of the scalp is seen with both dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis) and psoriasis.
MOST COMMON HAIR PROBLEMS :-
 .
.
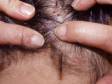
Head lice (pediculosis capitis) are highly contagious, and the most prominent symptom of a head lice infestation includes intense scalp itching.
The human head louse is a tiny insect that feeds on human blood. The female louse lays eggs (nits) on the hair shaft close to the scalp, and they become glued to the hair shaft.
The nits hatch about 8–10 days later and begin to feed with any remaining adults. The nits can stay alive for a long period of time off of the body, such as on hairbrushes, furniture, or linens.
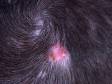
3. Ringworm, Scalp,( Tinea capitis )-
Infections of the scalp include bacterial infection of hair follicles (folliculitis), infestation of head lice (pediculosis capitis), and fungal infection of scalp ringworm (tinea capitis). Itching and excessive flaking of the scalp is seen with both dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis) and psoriasis.
MOST COMMON HAIR PROBLEMS :-
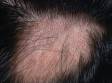
1. Alopecia areata -
 .
. - Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition resulting in hair loss.
- Genetic and environmental factors play a role in hair loss; the condition may be seasonal as well.
- Hair loss may be patchy or sparse and may involve the rest of the body in addition to the scalp.


- Tinea capitis is the medical term for ringworm, a very common fungal infection, of the scalp.
- There are no worms involved in scalp ringworm, rather the rash forms a scaly, round patch that sometimes clears or improves in the middle, thus looking like a ring.
- Ringworm can occur on other parts of the body, but scalp ringworm is commonly seen in children. It is contagious and is acquired by contact with infected people, animals, or objects (such as towels, combs, and pillows).
- Scalp ringworm should be treated (by a prescription medicine your doctor can prescribe) because it is contagious and because, if left untreated, the affected area can develop hair loss and sometimes another, more serious, infection called a kerion.
